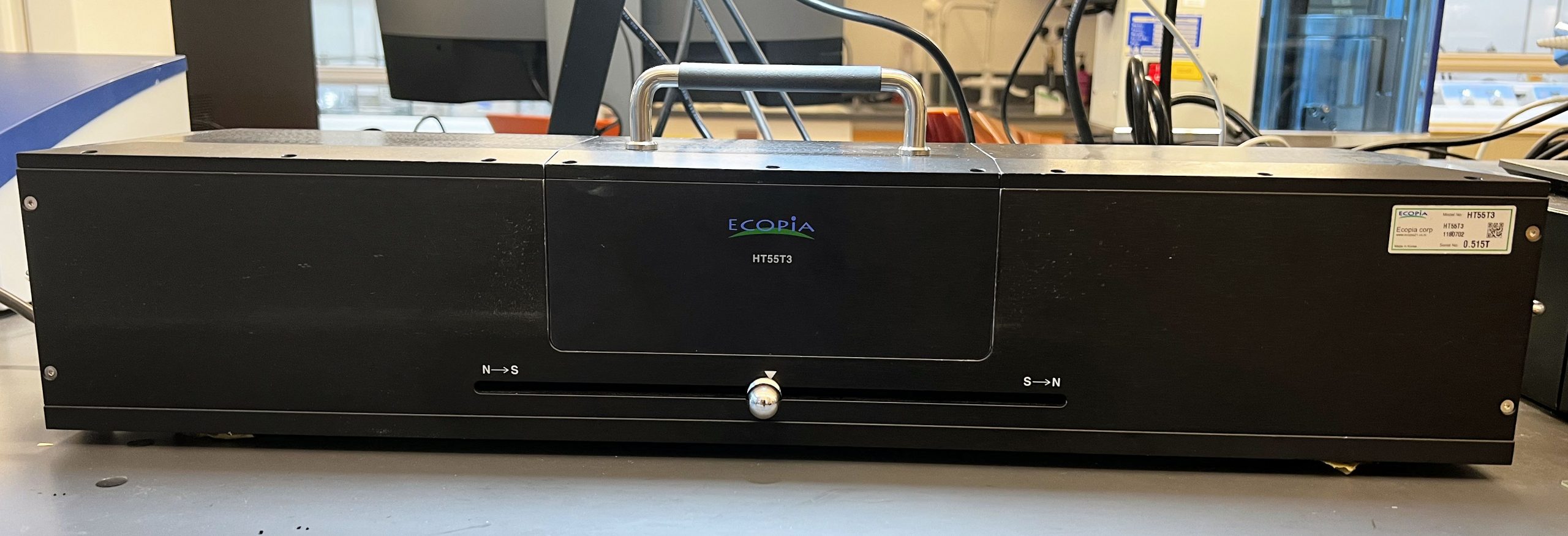
The Ecopia HMS-3000 Hall effect measurement system precisely measures carrier concentration, Sheet concentration, Mobility, Conductivity, Sheet resistance, average Hall coefficient, Resistivity, B-D Cross Hall Coefficient, A-C Cross Hall Coefficient, Alpha (Vertical/Horizontal ratio of resistance), and Magnetoresistance of a thin sample.
It is applicable for characterizing various materials, including semiconductors and compound semiconductors (both N Type & P Type) such as Si, Ge, SiGe, SiC, GaAs, InGaAs, InP, GaN, ZnO, TCOs, metals, etc., at temperatures of both 300K and 77K (room temperature and liquid nitrogen temperature).
The equipment utilizes the van der Pauw technique for these measurements, a method widely adopted for determining the Resistivity and Hall Coefficient of a sample. Its key advantage lies in its precision in assessing sample properties, irrespective of the sample’s shape, provided it’s roughly two-dimensional (meaning significantly thinner than its width) and the electrodes are placed around its perimeter. However, five conditions must be met for this technique to be effective:
- The sample must be flat and of uniform thickness.
- The sample must be free of isolated holes.
- The sample must be homogeneous and isotropic.
- All four contacts must be positioned at the sample’s edges.
- The contact area of each electrode should be at least ten times smaller than the total sample area.
The Ecopia HMS-3000 Hall Effect Measurement System has the following capabilities:
• Carrier Density from 107/cm3 to 1021/cm3
• Resistivity from 10-4 to 107 ohm-cm
• Mobility from 1 to 107 cm2/Vs
• Input DC Current from 1nA to 20 mA
• Output Voltage 12V
• Magnetic Flux Density 0.55T
• Sample Measurable Size 5mm x 5mm to 20mm x 20mm
• Sample Measurable Thickness: Less than 1.5 mm
• Sample Measurable Temperature at 77K and from RT to 623K (350 C)
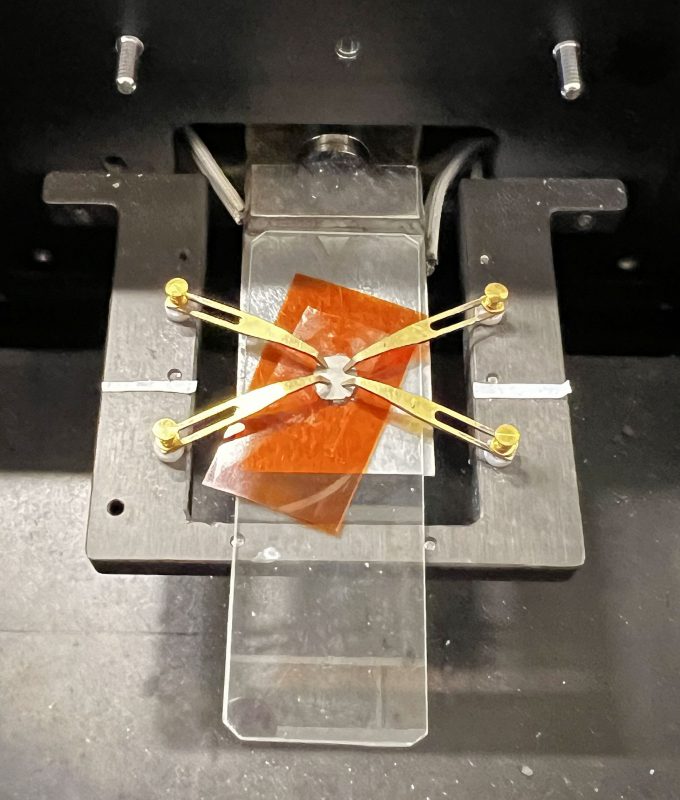
Examples of Materials Measured
Solar cells
OPVs, a:Si, µc-Si, CdTe, CuInGaSe (CIGS)
Organic electronics
OTFTs, Pentacene, Chalcogenides, OLEDs
Transparent conducting oxides
InSnO (ITO), ZnO, GaZnO, InGaZnO (IGZO)
III-V semiconductors
InP, InSb, InAs, GaN, GaP, GaSb, AIN based devices, high electron mobility transistors (HEMTs) and heterojunction bipolar transistors
II-VI semiconductors
CdS, CdSe, ZnS, ZnSe, ZnTe, HgCdTe
Elemental semiconductors
Ge, Si on insulator devices (SOI), SiC, doped diamond SiGe based devices: HBTs and FETs
Dilute magnetic semiconductors
GaMnAs, MnZnO
Half-Heusler compounds
TiNiSn, ZrNiSn, GdPtBi
Topological semi-metals
TaAs, WTe2, MoTe2
Topological insulators
Bi2Te3, Bi2Se3, Sb2Te3
Transition-metal Di-chalcogenides (TMDC)
WS2, WSe2, MoS2, HfS2
Other 2D materials
BN, graphene structures
Other conducting materials
Metal oxides
Organic and inorganic conductors
Metal Films and Coatings Thinner than 20 micrometers
High temperature superconductors