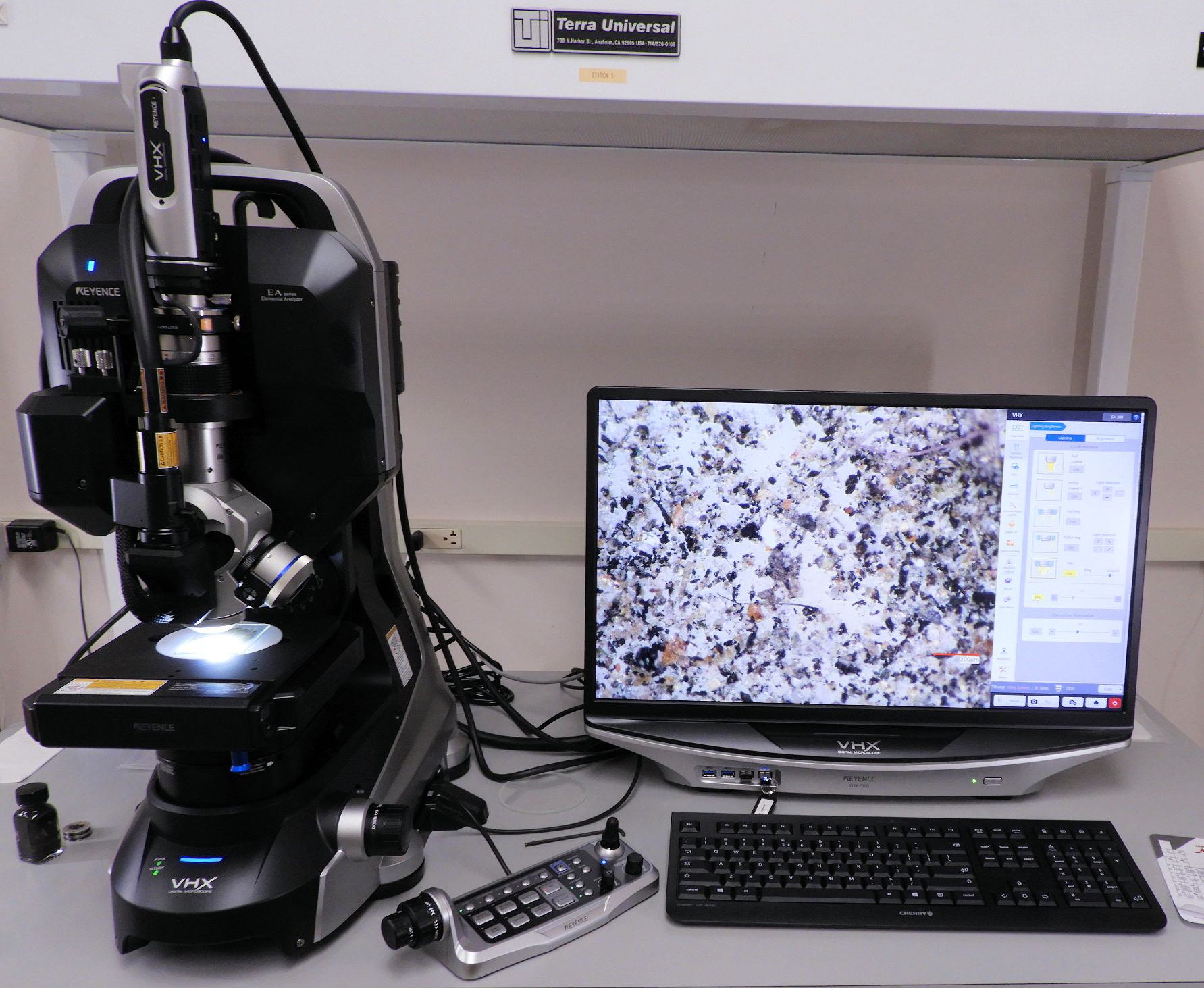
Keyence Capabilities
- 4K CMOS Image Sensor
- Zoom Magnification: 20X to 2000X
- Motorized Lens and Sample Stage
- 3D Image Construction: High depth of field at high optical resolution
- Color Information: Retained unlike SEM images, providing chemical phase information
- Large-Area Imaging: Stitching images together
- Lighting Options: Ring and co-axial lighting, quadrant ring lighting, quadrant through-the-lens lighting, mixed ring and co-axial lighting
- Calibrated Measurements: 2D and 3D distance measurements
- Particle and Grain Size Analyses: Advanced image analysis
- Surface Topography Profiles: Surface roughness measurement over lines and areas
- Integrated LIBS: Elemental analysis of small material volumes
- Small Particle Analysis: Environmental investigation
Example Studies
Keyence 3D Image of Roof Debris
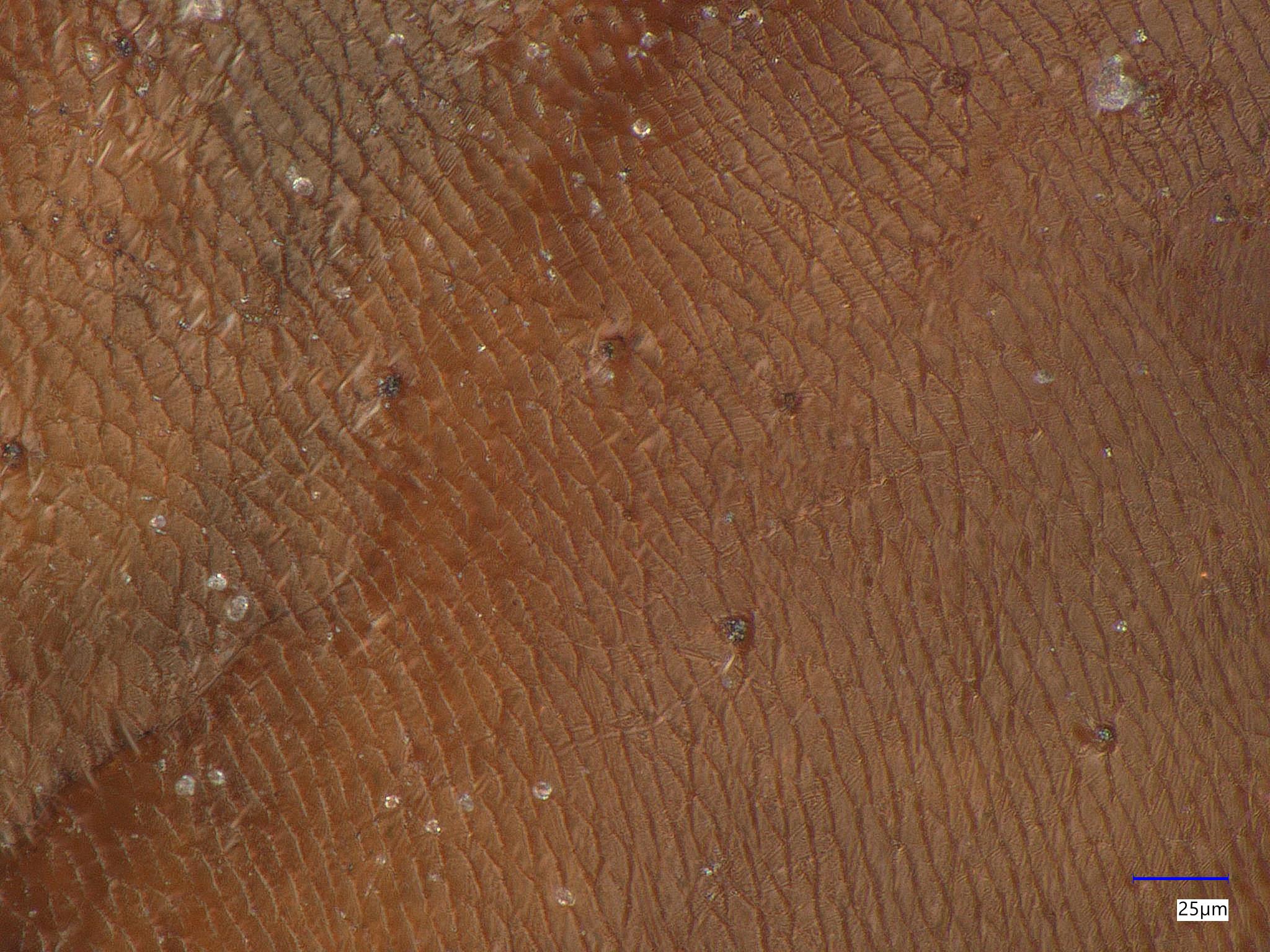
We tested industrial roof debris to identify sources of aluminum, zinc, and copper. The location was near heavy traffic and major highways. The 3D image showed tire wear particles, silicate particles, and organic fibers. By heating the debris to 250°C, we distinguished tire wear particles from bitumen. LIBS elemental analysis of 83 particles and fibers found aluminum mostly in aluminosilicates, two particles with low zinc concentrations in silicates, and one particle with low copper concentration in a silicate. The particles were likely wind-blown dust from a nearby mountain range. XPS analysis found more zinc on the immediate surfaces than LIBS, which analyzes deeper. The zinc residue was likely from zinc oxide vulcanization of tire rubbers, resulting in zinc oxide nanoparticles.
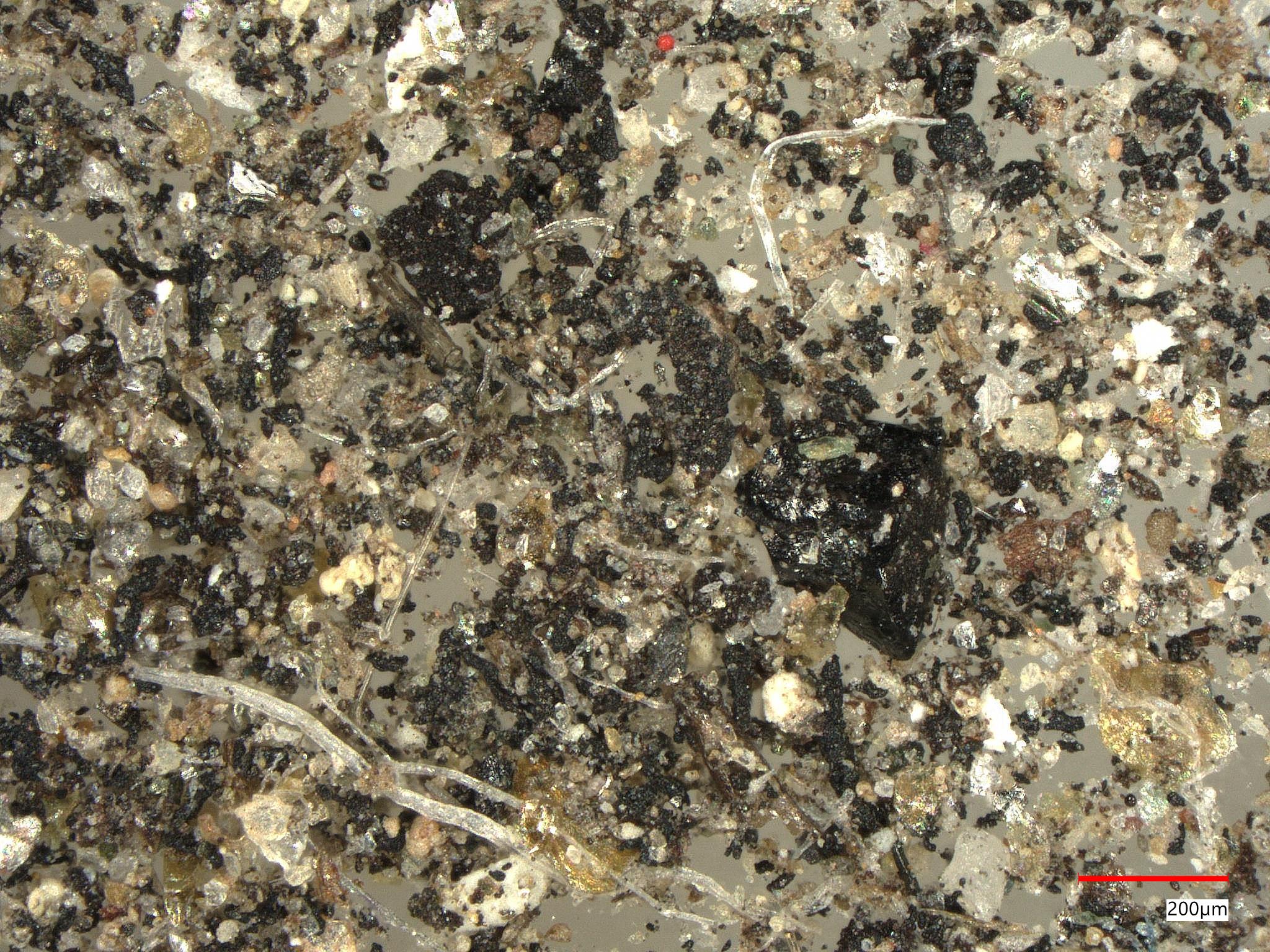

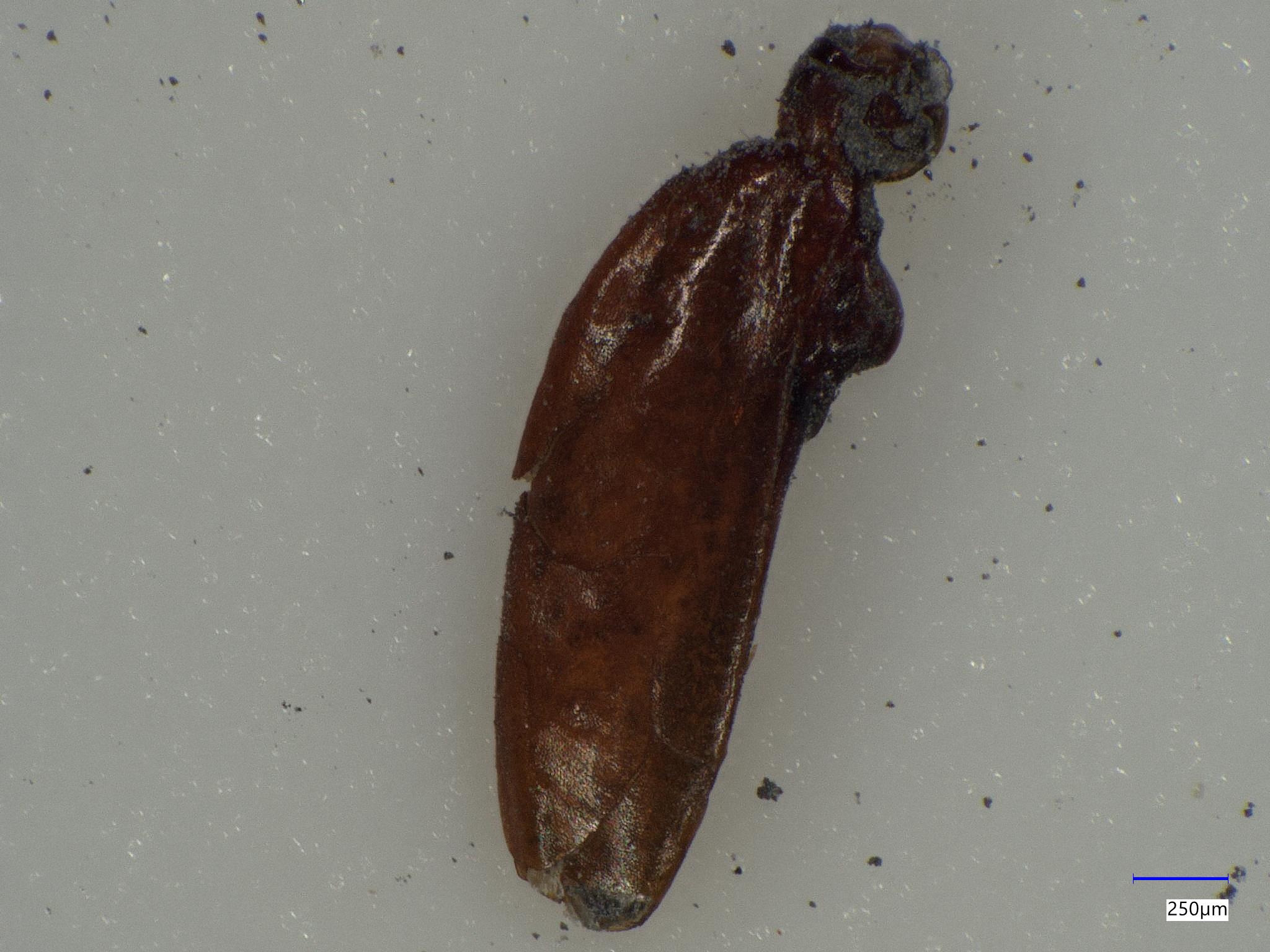
Foreign Object Debris in High-Value Battery Salt
We used Keyence 3D optical microscopy to examine debris in energy-storage device salts, finding a complete insect and pieces from other insects. The high-resolution texture images of the insect’s body and wings helped identify other insect fragments due to common surface textures and coloration. We also identified a smaller number of non-insect particles using LIBS.

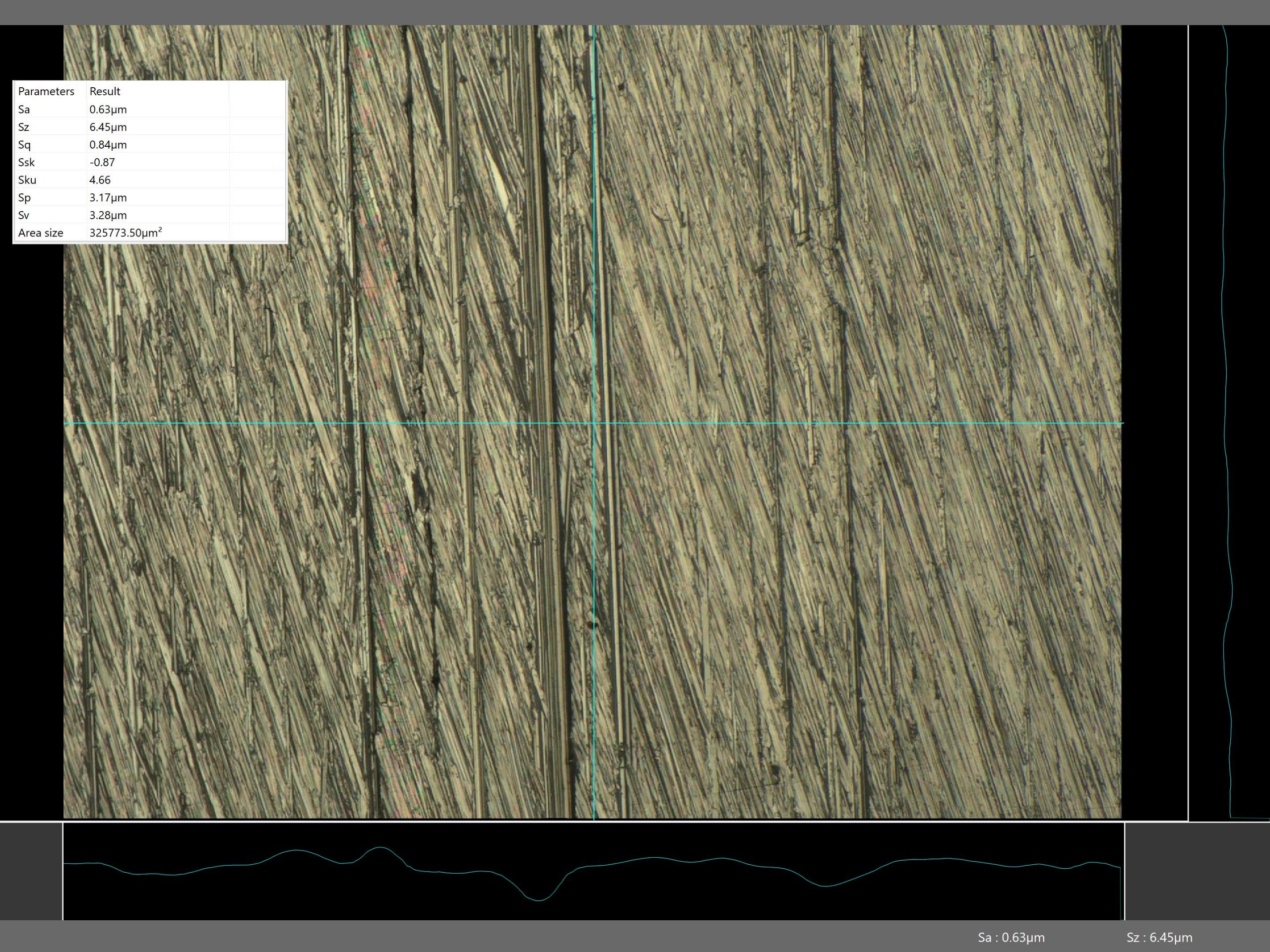
Surface Roughness Measurements
Surface roughness parameters can be measured along a line or area. The 3D focused surface can be referenced to a fitted plane for tilt correction or to fitted spheres or cylinders. Parameters measured include:
- Sa: Arithmetic mean deviation
- Sq: Root mean square deviation
- Ssk: Skewness
- Sku: Kurtosis
- Sp: Maximum peak height
- Sv: Maximum valley depth
- Sz: Sum of Sp and Sv
Example: The surface roughness parameters of a polished stainless steel square tube are measured using the Keyence VHX-7000N digital optical microscope.
Case Histories
Silicon Nitride Ceramic Analysis
Contact Us
Please contact us for any questions or to discuss how we can assist with your analysis needs.