The European Union (EU) through its RoHS regulations requires that most products sold in the EU must have upper limits on the following 10 restricted substances:
- Cadmium (Cd): < 100 parts per million (ppm) by weight
- Lead (Pb): < 1000 ppm
- Mercury (Hg) < 1000 ppm
- Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI): < 1000 ppm
- Polybrominated Biphenyls (PBB): < 1000 ppm
- Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDE): < 1000 ppm
- Bis(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP): < 1000 ppm
- Benzyl Butyl Phthalate (BBP): < 1000 ppm
- Dibutyl Phthalate (DBP): < 1000 ppm
- Diisobutyl Phthalate (DIBP): < 1000 ppm
Analysis Methods
All samples examined for RoHS compliance are analyzed with wavelength-dispersive x-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) to determine the concentrations of cadmium, lead, mercury, chromium, and bromine. This will actually provide the concentration for all elements heavier than oxygen. If the total chromium concentration is less than 1000 ppm, then it is not necessary to do further analysis to determine what fraction of the total chromium might be hexavalent chromium. If the chromium is in metallic form as part of a metal alloy, then further analysis may not be needed. However, if not, then x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis will be used to determine what fraction of the chromium is hexavalent chromium. If the bromine concentration is below 343 ppm, then there cannot be 1000 ppm of any of the PBBs. If the bromine concentration is below 322 ppm, then there cannot be 1000 ppm of any of the PBDEs.
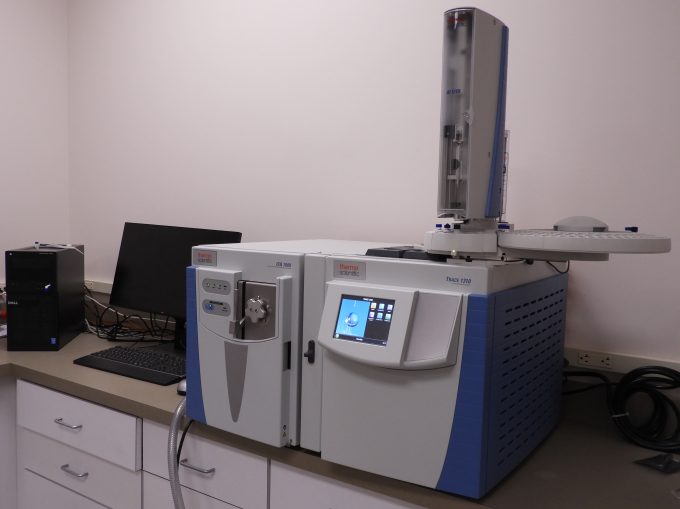
Polymers, organic substances, and many composite materials subject to RoHS compliance need to be analyzed for the restricted organic substances. This is done by using solvent extraction methods to remove the restricted organic substances from the polymer, organic substance, or composite material. The solvent-extract is then analyzed by gas chromatography – mass spectroscopy (GC-MS) to determine whether any of the restricted organic compounds are present. If they are, it needs to be determined whether their concentrations in the sample substance were greater than 1000 ppm or not. The extracted weight of the restricted bromine-containing organic determined from the concentration in the solvent as measured by GC-MS and the total solvent weight has to be divided by the original sample weight to determine the restricted substance weight in the original sample.