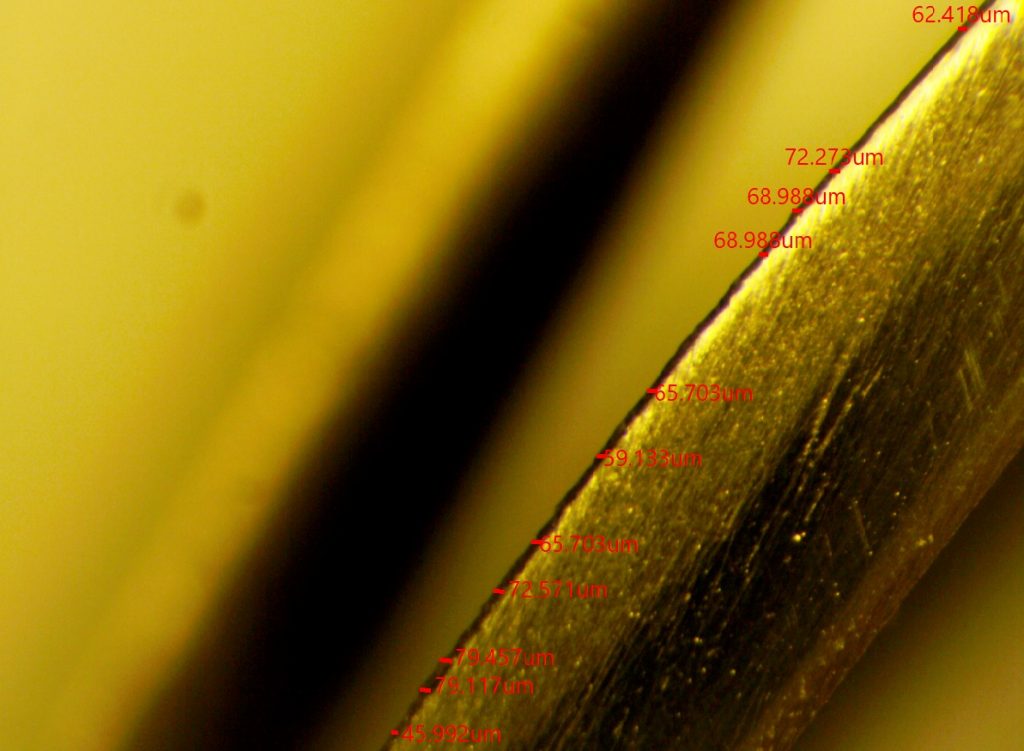
Below are some of the examples of thin film analysis performed by our lab.
XPS Analysis (10 nm depth, elemental and chemical bond analysis):
- Surface chemistry and film stoichiometry, especially subject to variation for sputtered or CVD films
- Elemental composition as a function of depth, useful to examine multilayer film structures such as anti-reflective coatings, metallization layers on ceramics for brazing, or coatings such as TiN on biomedical devices
- Interface contamination
- Surface hydration measurements
- Failure analysis of delamination problems
- Determine whether film layers have reacted or boundaries are sharp
- Diffusion as a function of temperature in vacuum
- Reaction of discrete film with other layers or with substrate as a function of temperature, such as due to brazing or soldering
- Reaction of film or multilayered film with heating in various gases
- Surface analysis of polymers, but cannot perform ion etching analysis of polymers
FTIR Analysis (1 – 2 micrometer depth, chemical bond analysis):
- Detect and identify thin organic or polymer film on metal or semiconductor surface
- Identify thin organic film used to prevent reactions of a thin film structure with the environment as in corrosion
- Identify plastic or polymer with metallization film
Thin Film Thickness Measurements:
- SEM or metallographic microscopy imaging of cross section
- Depth profile or angle-resolved XPS if very thin
Profilometry or Surface Roughness and Microscopy:
- Measure surface roughness
- 3-dimensional surface topography mapping
- Detection of defects as small as 500 nm
- Measurement of 2D and 3D distances
- Layer thickness measurements
Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) :
- Quickly determine the major composition of a thin film
- Quickly determine whether a material has such elements as aluminum, calcium, sodium, lead, or boron at elevated concentrations
Reactivity of Thin Film:
- TGA measurement of film weight gain due to reaction with gas as temperature is increased
- TGA testing of oxidation protection offered to substrate material by thin film or test for reactivity at higher temperatures and examine by XPS afterward
- DSC measurement of exothermal heat of reaction due to reaction of film with substrate or with other layers in multilayer structures, such as for intermetallic phase formation
- DSC measurement of endothermal heat of melting or of crystalline phase changes
- DSC measurement of exothermal heat of reaction with heating in a gas
- XPS substrate element diffusion through film to surface in active atmosphere conditions or upon heating
- Multilayer film interlayer reactions by depth profile XPS with exception of polymers
- Thickness measurement
- Grain size and orientation
- Detection of inclusions
- Uniformity
- Observable phases (carbides, intermetallic phases, graphite micro clusters, etc.)
Adhesion Failures:
- Failure analysis of peeled or delaminated thin film for locus of failure and detection of contamination, hydration, reacted layer, or other causes of failure using XPS and FTIR
- Examination with metallographic microscopy or SEM to determine mode and locus of failure