At Anderson Materials Evaluation, we utilize many techniques to analyze surface & interface contamination and cleanliness.
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy or XPS or ESCA:
- Quantitative elemental composition of surface contamination
- Surface contamination chemistry with chemical phase identification
- Extremely high sensitivity with an analysis depth of 10 nm and sensitivity for less than 0.1 monatomic layer
- Verification of surface cleanliness
- Measure silicone surface concentration and relative chain length to determine effect in weakening adhesive bonding to a surface or interface, sealant integrity, wetting problems, or as a source of silicone contamination
- Provide silicone and fluorocarbon contamination detection test kits to be examined by XPS for facility and oven contamination evaluations
- Surface chemistry changes caused by cleaning agents, both improvements and residues left
- Ion sputter gun removal of surface contamination to judge its thickness
- Quantitative elemental and chemical phase identification of interfacial contamination after adhesive failure, peel, or pull test
- Interphase chemistry of interfaces with adhesive bonding – adhesives often have different compositions near interfaces
- Depth profile through thin layers at a surface for elemental analysis as a function of depth
- Analyze residues left after evaporating water or other solvents
- Identify plasticizers, fire retardants, and cross-linking agents in polymers or plastics that migrate to surfaces and interfaces
- Examine surfaces after anodization and etching processes to determine if the surfaces were properly cleaned
FTIR or Infrared Spectroscopy for Surface Contamination:
- Identification of organic functional groups and some inorganic functional groups in thicker contaminant layers using ATR or specular reflectance for greater surface sensitivity
- Bulk or near-surface (1 -2 micrometers deep) organic material composition for comparison to surface organic composition
- Identify plasticizer or fire-retardant segregated to the surface of a plastic/polymer material
GC-MS or Gas Chromatography – Mass Spectroscopy
- Wipe surfaces with swabs and remove and analyze the contaminants from the swab for high-sensitivity GC-MS analysis at the ppb concentration level.
- Rinse a surface with a solvent and analyze the rinse solvent to find what was on the surface.
Microscopic Examinations for Surface Contamination:
- SEM with digital imaging to reveal surface inclusions and surface deposits
- Inspection microscope, digital imaging
- Metallographic microscope, digital imaging, Nomarski phase contrast
Profilometry or Surface Roughness and Microscopy:
- Measure surface roughness
- 3-dimensional surface topography mapping
- Detection of defects as small as 500 nm
- Measurement of 2D and 3D distances
- Layer thickness measurements
Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) :
- Quickly determine the major composition of a material
- Quickly determine whether a material has such elements as aluminum, calcium, sodium, lead, or boron at elevated concentrations
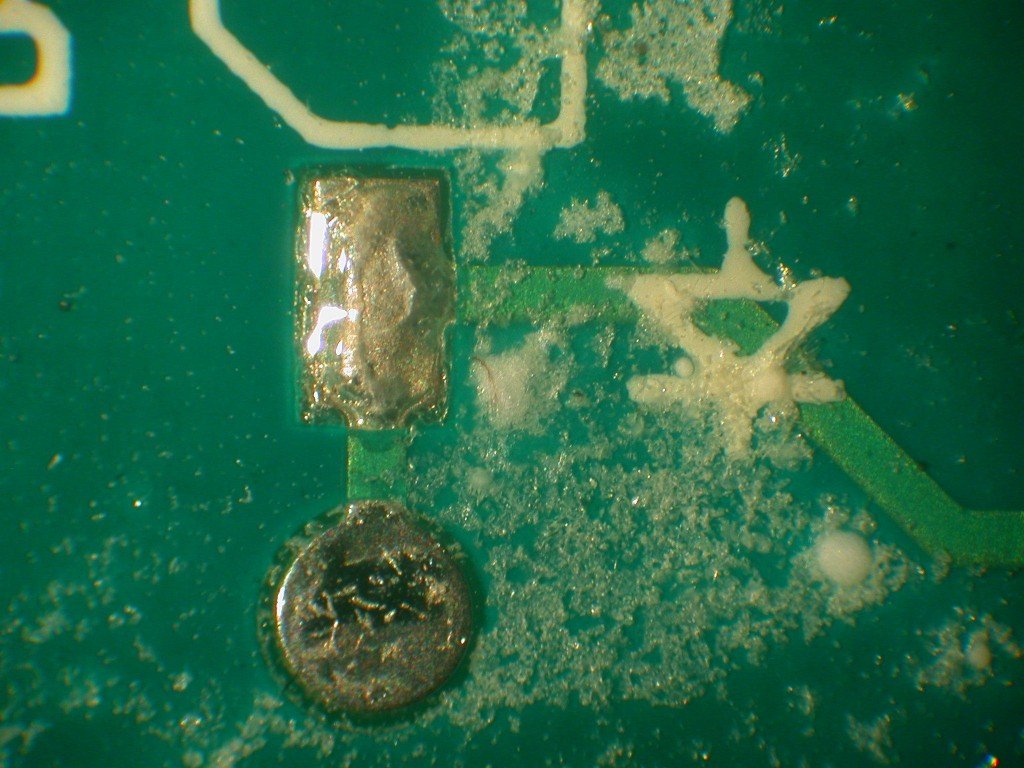
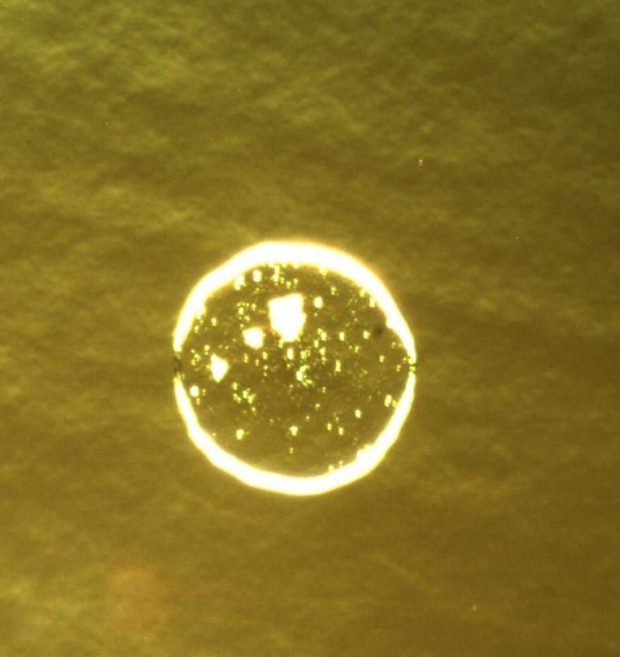


Effect of interfacial contamination on adhesion to the interface using pull tests.
Surface cleaning technique evaluations:
- CO2 snow jet cleaning, in-house capability, but learn more about CO2 snow jet cleaning at Applied Surface Technologies
- Solvent-based cleaning
- Check cleaning effectiveness with above analytical capabilities
- Determine changes in surface chemistry of plastics caused by plasma cleaning
Corrosion Testing for Surface Contamination:
- Identify corrosion products and causes.
Applications:
- Electronics contamination
- Packaging materials contamination
- Medical device contamination
- Composite materials fibers and particulates contamination affecting matrix bonding
- Adhesive bonding preparation and cause of bonding failures
- Corrosion due to contamination
Case Histories
Solving a Polymer Sealing Problem with XPS Analysis
Silicone Detection on the Surface of an Acrylic Adhesive/Polyimide Tape