Overview
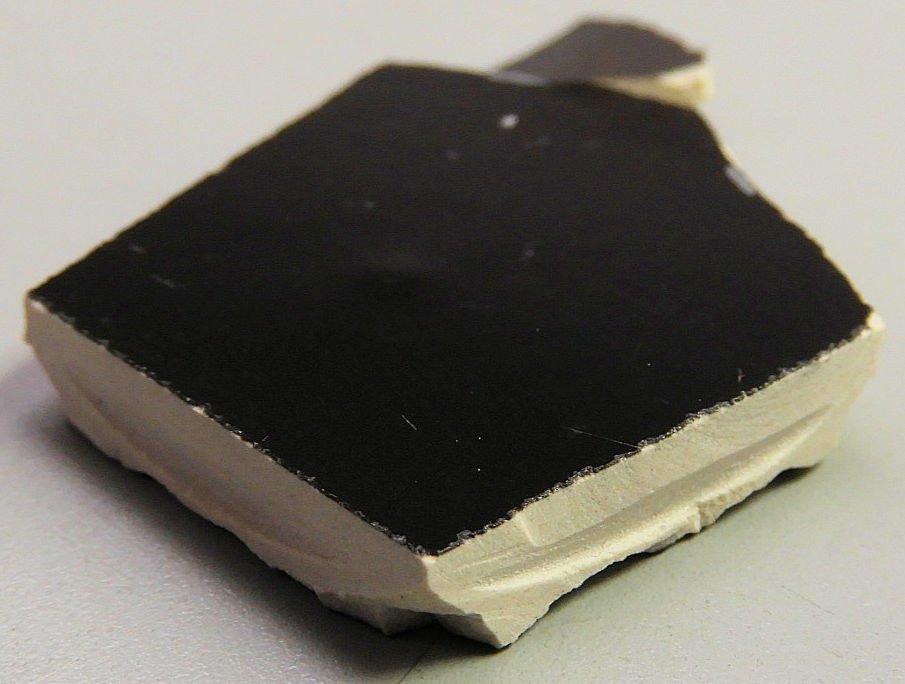
We analyzed a black ceramic dinner plate to determine if it contains heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, and mercury. The plate is composed of at least two different materials: an outer hard black glaze and an inner softer ceramic material. Many people have concerns about the safety of their homeware. At AME, we are here to help you and/or your business with your heavy metals concerns.
Lead in Ceramic Analysis Method
- WD-XRF Analysis:
- This technique examines a combination of the black glaze layer and the interior ceramic material. The depth of detection varies for different metals, being several times the thickness of the glaze layer for cadmium and about twice that for lead and mercury.
- The goal is to establish the presence of lead, cadmium, mercury, or other hazardous elements in the materials.
- XPS Surface Analysis:
- We then use XPS surface analysis if heavy metals are detected in the sample. We use it to see if these metals are present on the surface where they might come into contact with food.
WD-XRF Analysis Results
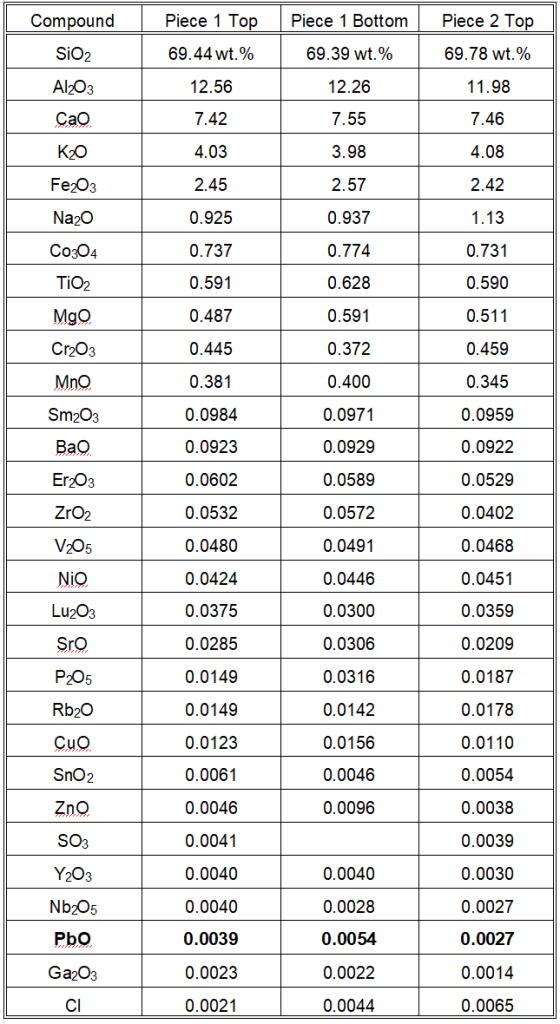
- We performed analysis on two pieces of the same plate, with both the top (eating surface) and bottom black glaze analyzed.
- We did not detect cadmium or mercury.
- AME labs detected lead at 0.0039, 0.0054, and 0.0027 weight percent (wt.%) PbO, equivalent to 39, 54, and 27 parts per million (ppm) by weight.
Lead in Ceramic XPS Surface Analysis Results
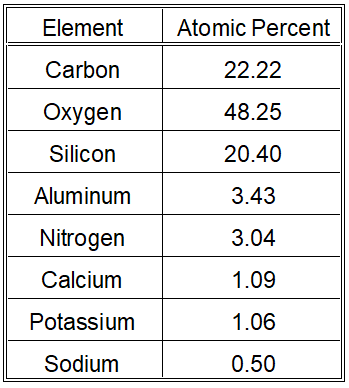
- XPS analysis examines the outer 20 nm of the surface.
- Despite the a thorough surface cleaning, we were able to detect hydrocarbons.
- We did not detect lead on the surface, suggesting the lead concentration is below 0.003 weight percent (30 ppm).
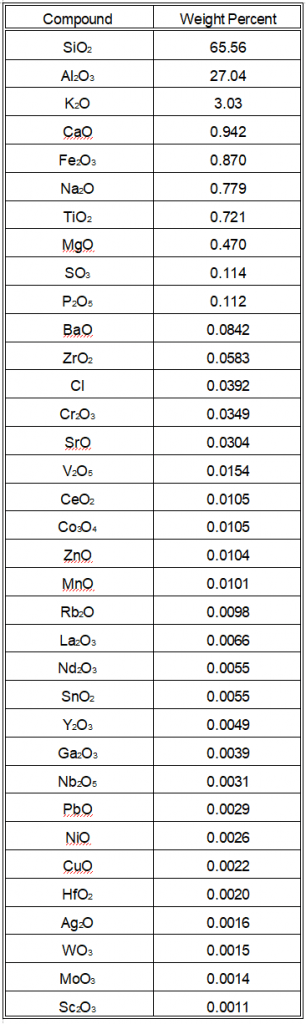
XRF Analysis of Interior Ceramic Material
- We removed the black glaze from one piece to analyze the interior ceramic material.
- The interior material showed a slight reduction in silica and an increase in alumina, consistent with expectations.
- The lead content decreased from 39 ppm to 29 ppm after removing the glaze, within the estimated error margin.
Lead in Ceramic Conclusions
- The average lead content in the plate, including both glaze and interior, is about 40 ppm PbO, with individual measurements ranging from 27 to 54 ppm.
- The lead content in the interior ceramic material alone is around 29 ppm.
- XPS analysis indicates the lead concentration on the surface is below 30 ppm, aligning with the XRF results.
- We concluded that there is potential for user exposure to lead in the ceramic dinner plate. The lead may not be fully isolated by the glaze.
Contact Us
For more information or if you have any concerns about the safety of your ceramic dinnerware, please contact us at Anderson Materials Evaluation, Inc. We are here to help you with your materials analysis needs.