Graphitic corrosion poses a serious threat to grey cast iron water pipes, impacting their structural integrity over time. Unlike visible surface rust, this type of corrosion occurs beneath the surface, making it difficult to detect and potentially leading to catastrophic failures, especially in pipes carrying water at high pressures.
SEM Images
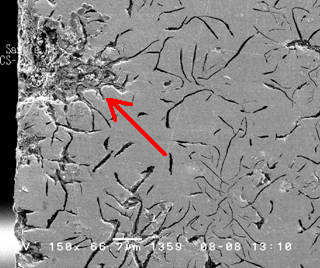
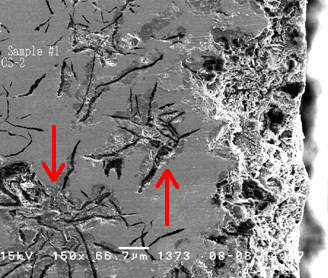
These SEM (Scanning Electron Microscope) images provide cross-sectional views of a grey cast iron water pipe:
- The first image shows the outer surface that was buried in moist soil. It reveals visible damage penetrating the pipe wall due to graphitic corrosion.
- The second image displays the inner surface exposed to potable water. Here, corrosive attack is evident, causing roughening and thinning of the pipe wall. Graphitic corrosion is clearly visible around clusters of graphite flakes, causing metal loss through galvanic action.
Impact of Graphitic Corrosion
Graphitic corrosion transforms parts of the pipe’s wall thickness into brittle graphite, significantly weakening its mechanical strength. This internal damage is critical as it can lead to unexpected pipe failures, especially under high water pressures.
Significance of Detection
Detecting graphitic corrosion is challenging because it occurs beneath the surface and is not visible during routine inspections. This hidden deterioration underscores the importance of advanced inspection techniques beyond visual examination. Early detection is crucial to prevent failures and ensure the long-term reliability of water distribution systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, graphitic corrosion represents a substantial risk to grey cast iron water pipes. Its ability to weaken the structural integrity of pipes, combined with its hidden nature, highlights the necessity for thorough inspection methods. By employing advanced techniques such as SEM analysis, we can better understand and mitigate the effects of graphitic corrosion, safeguarding water infrastructure against potential failures.
This understanding is vital for maintaining the safety and reliability of water distribution networks, ensuring they can withstand the demands of their operational environments without compromising public health or infrastructure integrity.