We determine the bulk density and porosity of monolithic materials using the Archimedes method, specifically Method 1 of DIN EN 623-2 and Method A of ASTM D792. This method is suitable for apparent porosity measurements greater than 1% and is essentially the same as ISO 1183.
Method Overview
- Dry the Test Sample: The sample is dried in an oven.
- Degas the Test Sample: The sample is degassed under reduced pressure.
- Immerse in Water: The sample is immersed in water, and the mass of the soaked test piece is determined.
Note: This method is not necessary for materials with an average pore size greater than 200 µm. For polymers with a specific gravity less than 1, we use isopropyl alcohol instead of water.
Sample Preparation
- Three test samples are typically prepared.
- Approximately 1 to 3 gm of a sample is commonly used for the analysis.

Apparatus
- Drying Oven: Maintains a temperature of 110 °C ± 5 °C for drying samples.
- Balance: An analytical balance with a density measurement apparatus to determine the mass of the immersed and soaked test samples.
- Vacuum Pump: Reduces pressure to 0.040 Pa (0.0040 mbar) for degassing.
- Immersion Liquid: Distilled water with a few drops of wetting agent to prevent air bubbles.
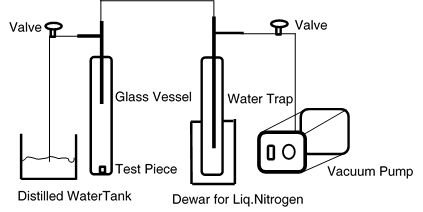
Procedure
- Determine the Mass of Dry Samples:
- Dry samples in an oven at 110°C overnight.
- Cool samples in a desiccator to room temperature, then weigh immediately (m1).
- Soak the Test Samples:
- Place the sample in a glass vessel and evacuate to less than 2500 Pa for 15-20 minutes.
- Introduce distilled water, submerging the sample, and maintain reduced pressure for 30-40 minutes.
- Allow the vessel to return to ambient pressure for an additional 30-40 minutes.
- Determine the Mass of Immersed Samples:
- Weigh the sample while it is suspended and fully immersed in water (m2).
- Determine the Mass of Soaked Samples in Air:
- Quickly wipe the sample to remove surface droplets without drawing liquid from the pores.
- Weigh the sample immediately (m3).


Calculating Density and Porosity
Using the three weight measurements, we can calculate:
- Solid Material Density
- Bulk Apparent Sample Density
- Percentage of Porosity Volume
This method, ASTM D792-20, provides a comprehensive understanding of the solid material’s lattice density, average density, and porosity percentage.
For more detailed information or any inquiries, please contact us.
When Porosity is not an Issue
ASTM C693 Standard Test Method for Density of Glass by Buoyancy is a simpler method for determining a materials’ density by buoyancy in water. It can be adapted to another liquid of known density such as isopropyl alcohol for polymers of lower density than water.